Description
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
BOD – biochemical oxygen demand – is an expression for the quantity of oxygen required for biological degradation of organic matter in a waste water sample. BOD measurement is therefore used as a basis for the detection of biologically degradable organic matter in water. The difference between BOD and chemical oxygen demand (COD) is that COD additionally registers biologically non-degradable organic matter. BOD measurement is therefore an important measurement of the effects of domestic and industrial waste water on sewage plants and outflow points.
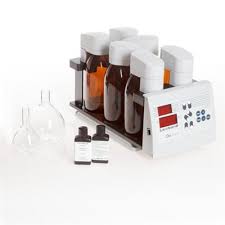
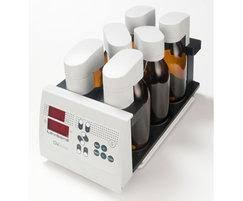
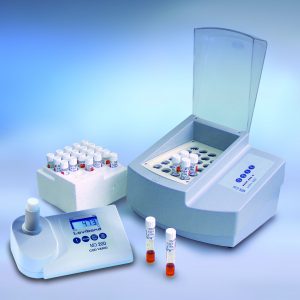
OxiDirect Principle
Respirometric methods provide direct measurements of the oxygen consumed by microorganisms from an air or oxygen-enriched environment in a closed vessel under conditions of constant temperature and agitation. Carbon dioxide produced metabolically by the bacteria is chemically bound by the potassium hydroxide solution contained in the seal cup in the bottle. The result is a pressure drop in the system, which is directly proportional to the BOD value and is measured by the Lovibond® BOD sensor. The BOD level is then displayed directly in mg/l. The BOD values are stored in the sensor memory and can be called up on the large-format display at any time without the need for time-consuming conversion using factors. This means that test series that end on a Sunday can be evaluated during the following week without any problem. The measurement period is user-selectable between 1 and 28 days to suit the application. While short measurement periods are useful for scientific applications, standard BOD measurements typically extend over a period of 5 days – and manometric determination of OECD, for example, generally takes place over a period of 28 days.
Product Specifications
| Dimensions | 230x195x375mm (HxWxD) |
| Range | 0-40mg/l, 0-80mg/l, 0-200mg/l, 0-400mg/l, 0-800mg/l, 0-2000mg/l, 0-4000mg/l |
Was the Camlab water BOD CW7000 DIRECT READING APPARATUS
Requires incubation of the whole unit for the test to be done